Modeling Trajectory-level Behaviors using Time Varying Pedestrian Movement Dynamics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17815/CD.2018.15Keywords:
pedestrians, crowds, behavior learning, pedestrian dynamics, multi-agentAbstract
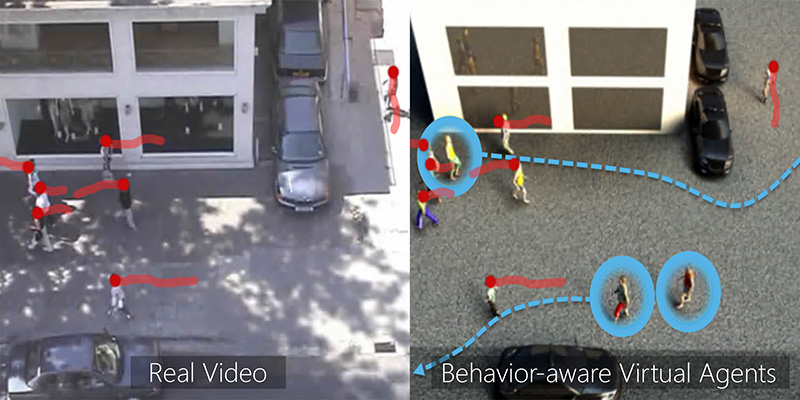
We present a novel interactive multi-agent simulation algorithm to model pedestrian movement dynamics. We use statistical techniques to compute the movement patterns and motion dynamics from 2D trajectories extracted from crowd videos. Our formulation extracts the dynamic behavior features of real-world agents and uses them to learn movement characteristics on the fly. The learned behaviors are used to generate plausible trajectories of virtual agents as well as for long-term pedestrian trajectory prediction. Our approach can be integrated with any trajectory extraction method, including manual tracking, sensors, and online tracking methods. We highlight the benefits of our approach on many indoor and outdoor scenarios with noisy, sparsely sampled trajectory in terms of trajectory prediction and data-driven pedestrian simulation.References
Bera, A., Kim, S., Manocha, D.: Realtime anomaly detection using trajectory-level crowd behavior learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 50-57 (2016)
Wolinski, D., Guy, S., Olivier, A.H., Lin, M., Manocha, D., Pettré, J.: Parameter estimation and comparative evaluation of crowd simulations. In: Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 33, pp. 303-312. The Eurographics Association and Blackwell Publishing Ltd. (2014)
Kim, S., Bera, A., Manocha, D.: Interactive crowd content generation and analysis using trajectory-level behavior learning. In: Multimedia (ISM), 2015 IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 21-26. IEEE (2015)
Bera, A., Kim, S., Manocha, D.: Online parameter learning for data-driven crowd simulation and content generation. Computers & Graphics 55, 68-79 (2016)
Reynolds, C.W.: Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model. In: SIGGRAPH '87, pp. 25-34. ACM, New York, NY, USA (1987). doi:10.1145/37401.37406
Pelechano, N., Allbeck, J.M., Badler, N.I.: Controlling individual agents in high-density crowd simulation. In: Symposium on Computer animation, pp. 99-108 (2007)
Helbing, D., Molnár, P.: Social force model for pedestrian dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 51, 4282-4286 (1995)
van den Berg, J., Guy, S.J., Lin, M., Manocha, D.: Reciprocal n-body collision avoidance. In: Robotics Research: 14th ISRR (STAR), vol. 70, pp. 3-19 (2011)
Karamouzas, I., Overmars, M.: Simulating and evaluating the local behavior of small pedestrian groups. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18(3), 394-406 (2012)
Ondřej, J., Pettré, J., Olivier, A.H., Donikian, S.: A synthetic-vision based steering approach for crowd simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 29(4), 123:1-123:9 (2010)
Treuille, A., Cooper, S., Popović, Z.: Continuum crowds. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2006, pp. 1160-1168. ACM (2006)
Narain, R., Golas, A., Curtis, S., Lin, M.C.: Aggregate dynamics for dense crowd simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(5), 122:1-122:8 (2009)
Zhang, J., Klingsch, W., Schadschneider, A., Seyfried, A.: Ordering in bidirectional pedestrian flows and its influence on the fundamental diagram. J. Stat. Mech. 2012(02), P02002 (2012)
Burghardt, S., Klingsch, W., Seyfried, A.: Analysis of flow-influencing factors in mouths of grandstands. In: Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics, vol. 4 (2012)
Kretz, T., Grnebohm, A., Schreckenberg, M.: Experimental study of pedestrian flow through a bottleneck. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment p. P10014 (2006)
Seyfried, A., Steffen, B., Klingsch, W., Boltes, M.: The fundamental diagram of pedestrian movement revisited. J. Stat. Mech. (10) (2005)
Narang, S., Best, A., Curtis, S., Manocha, D.: Generating pedestrian trajectories consistent with the fundamental diagram based on physiological and psychological factors. PLoS ONE 10(4), e0117856 (2015). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117856
Lee, K.H., Choi, M.G., Lee, J.: Motion patches: Building blocks for virtual environments annotated with motion data. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 898-906 (2006). doi:10.1145/1141911.1141972
Yersin, B., Maïm, J., Pettré, J., Thalmann, D.: Crowd patches: populating large-scale virtual environments for real-time applications. In: Interactive 3D graphics and games, pp. 207-214 (2009)
Lee, K.H., Choi, M.G., Hong, Q., Lee, J.: Group behavior from video: a data-driven approach to crowd simulation. In: Symposium on Computer Animation, pp. 109-118 (2007)
Li, Y., Christie, M., Siret, O., Kulpa, R., Pettré, J.: Cloning crowd motions. In: Proc. of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA '12, pp. 201-210 (2012). URL http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2422356.2422385
Kapadia, M., Chiang, I.k., Thomas, T., Badler, N.I., Kider Jr., J.T.: Efficient motion retrieval in large motion databases. In: Proc. of the ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, pp. 19-28 (2013). doi:10.1145/2448196.2448199
Lerner, A., Fitusi, E., Chrysanthou, Y., Cohen-Or, D.: Fitting behaviors to pedestrian simulations. In: Symp. on Computer Animation, p. 199–208 (2009)
Guy, S.J., van den Berg, J., Liu, W., Lau, R., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: A statistical similarity measure for aggregate crowd dynamics. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(6), 190:1-190:11 (2012). doi:10.1145/2366145.2366209
Wolinski, D., Guy, S.J., Olivier, A.H., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D., Pettré, J.: Parameter estimation and comparative evaluation of crowd simulations. In: Eurographics (2014)
Berseth, G., Kapadia, M., Haworth, B., Faloutsos, P.: Steerfit: Automated parameter fitting for steering algorithms. In: Eurographics/ ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation (2014). doi:10.2312/sca.20141129
Charalambous, P., Karamouzas, I., Guy, S.J., Chrysanthou, Y.: A data-driven framework for visual crowd analysis. Computer Graphics Forum 33(7), 41-50 (2014). doi:10.1111/cgf.12472
Zhang, K., Zhang, L., Yang, M.H.: Real-time compressive tracking. In: ECCV, pp. 864-877 (2012)
Bera, A., Kim, S., Manocha, D.: Efficient trajectory extraction and parameter learning for data-driven crowd simulation. In: Proceedings of Graphics Interface (2015)
Jordao, K., Pettré, J., Christie, M., Cani, M.P.: Crowd Sculpting: A space-time sculpting method for populating virtual environments. Computer Graphics Forum 33(2), 351-360 (2014). doi:10.1111/cgf.12316
Kwon, T., Lee, K.H., Lee, J., Takahashi, S.: Group motion editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 27(3), 80:1-80:8 (2008). doi:10.1145/1360612.1360679
Cui, J., Zha, H., Zhao, H., Shibasaki, R.: Tracking multiple people using laser and vision. In: Proc. of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2116-2121. IEEE (2005)
Kratz, L., Nishino, K.: Tracking pedestrians using local spatio-temporal motion patterns in extremely crowded scenes. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on (99), 1–1 (2011)
Bruce, A., Gordon, G.: Better motion prediction for people-tracking. In: Proc. of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), New Orleans, USA (2004)
Gong, H., Sim, J., Likhachev, M., Shi, J.: Multi-hypothesis motion planning for visual object tracking (2011)
Liao, L., Fox, D., Hightower, J., Kautz, H., Schulz, D.: Voronoi tracking: Location estimation using sparse and noisy sensor data. In: IROS (2003)
Luber, M., Stork, J., Tipaldi, G., Arras, K.: People tracking with human motion predictions from social forces. In: Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 464-469 (2010)
Mehran, R., Oyama, A., Shah, M.: Abnormal crowd behavior detection using social force model. In: Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,CVPR, pp. 935-942 (2009)
Pellegrini, S., Ess, A., Schindler, K., Van Gool, L.: You'll never walk alone: Modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In: ICCV, pp. 261-268 (2009)
Bera, A., Manocha, D.: Reach: Realtime crowd tracking using a hybrid motion model. ICRA (2015)
Yamaguchi, K., Berg, A., Ortiz, L., Berg, T.: Who are you with and where are you going? In: Proc. of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1345-1352 (2011). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995468
Fulgenzi, C., Spalanzani, A., Laugier, C.: Dynamic obstacle avoidance in uncertain environment combining pvos and occupancy grid. In: Robotics and Automation, 2007 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 1610-1616 (2007). doi:10.1109/ROBOT.2007.363554
Li, T., Chang, H., Wang, M., Ni, B., Hong, R., Yan, S.: Crowded scene analysis: A survey. Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, IEEE Transactions on 25(3), 367-386 (2015)
Borges, P., Conci, N., Cavallaro, A.: Video-based human behavior understanding: A survey. Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, IEEE Transactions on 23(11), 1993-2008 (2013). doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2013.2270402
Hu, W., Tan, T., Wang, L., Maybank, S.: A survey on visual surveillance of object motion and behaviors. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, IEEE Transactions on 34(3), 334-352 (2004)
Kim, S., Bera, A., Manocha, D.: Interactive crowd content generation and analysis using trajectory-level behavior learning. Tech. rep., University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (2015)
Zen, G., Ricci, E.: Earth mover's prototypes: A convex learning approach for discovering activity patterns in dynamic scenes. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on, pp. 3225-3232 (2011). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995578
Solmaz, B., Moore, B.E., Shah, M.: Identifying behaviors in crowd scenes using stability analysis for dynamical systems. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on 34(10), 2064-2070 (2012)
Mehran, R., Oyama, A., Shah, M.: Abnormal crowd behavior detection using social force model. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, pp. 935-942 (2009). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206641
Pellegrini, S., Gall, J., Sigal, L., Gool, L.: Destination flow for crowd simulation. In: Computer Vision – ECCV 2012. Workshops and Demonstrations, vol. 7585, pp. 162-171 (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-33885-4_17
Zhou, B., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Understanding collective crowd behaviors: Learning a mixture model of dynamic pedestrian-agents. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE Conference on, pp. 2871-2878 (2012). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248013
Sun, L., Li, X., Qin, W.: Simulating realistic crowd based on agent trajectories. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 24(3-4), 165-172 (2013). doi:10.1002/cav.1507
Enzweiler, M., Gavrila, D.M.: Monocular pedestrian detection: Survey and experiments. PAMI pp. 2179-2195 (2009)
McLachlan, G.J., Krishnan, T.: The EM Algorithm and Extensions (Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics), 2 edn. Wiley-Interscience (2008)
Kim, S., Bera, A., Best, A., Chabra, R., Manocha, D.: Interactive and adaptive data-driven crowd simulation. In: IEEE Virtual Reality (VR), pp. 29-38. IEEE (2016)
Curtis, S., Manocha, D.: Pedestrian simulation using geometric reasoning in velocity space (in PEDS, 2012)
Kim, S., Guy, S.J., Liu, W., Lau, R.W., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: Predicting pedestrian trajectories using velocity-space reasoning. In: WAFR (2012)
Lerner, A., Chrysanthou, Y., Lischinski, D.: Crowds by example. Computer Graphics Forum 26(3), 655-664 (2007). doi:10.1111/j.1467-8659.2007.01089.x
Bera, A., Kim, S., Randhavane, T., Pratapa, S., Manocha, D.: Glmp-realtime pedestrian path prediction using global and local movement patterns. ICRA (2016)
Brscic, D., Kanda, T., Ikeda, T., Miyashita, T.: Person position and body direction tracking in large public spaces using 3d range sensors. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems 43(6), 522-534 (2013)
Kim, S., Guy, S.J., Liu, W., Wilkie, D., Lau, R.W., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: Brvo: Predicting pedestrian trajectories using velocity-space reasoning. The International Journal of Robotics Research p. 0278364914555543 (2014)
Reynolds, T.R.: Stride length and its determinants in humans, early hominids, primates, and mammals. American Journal of Physical Anthropology (1987)
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Aniket Bera, Sujeong Kim, Dinesh Manocha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to Collective Dynamics agree to publish their articles under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license.
This license allows:
Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
for any purpose, even commercially.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Authors retain copyright of their work. They are permitted and encouraged to post items submitted to Collective Dynamics on personal or institutional websites and repositories, prior to and after publication (while providing the bibliographic details of that publication).








